Zebrafish Axis Formation: BMP7's Crucial Role Explained
<!DOCTYPE html>
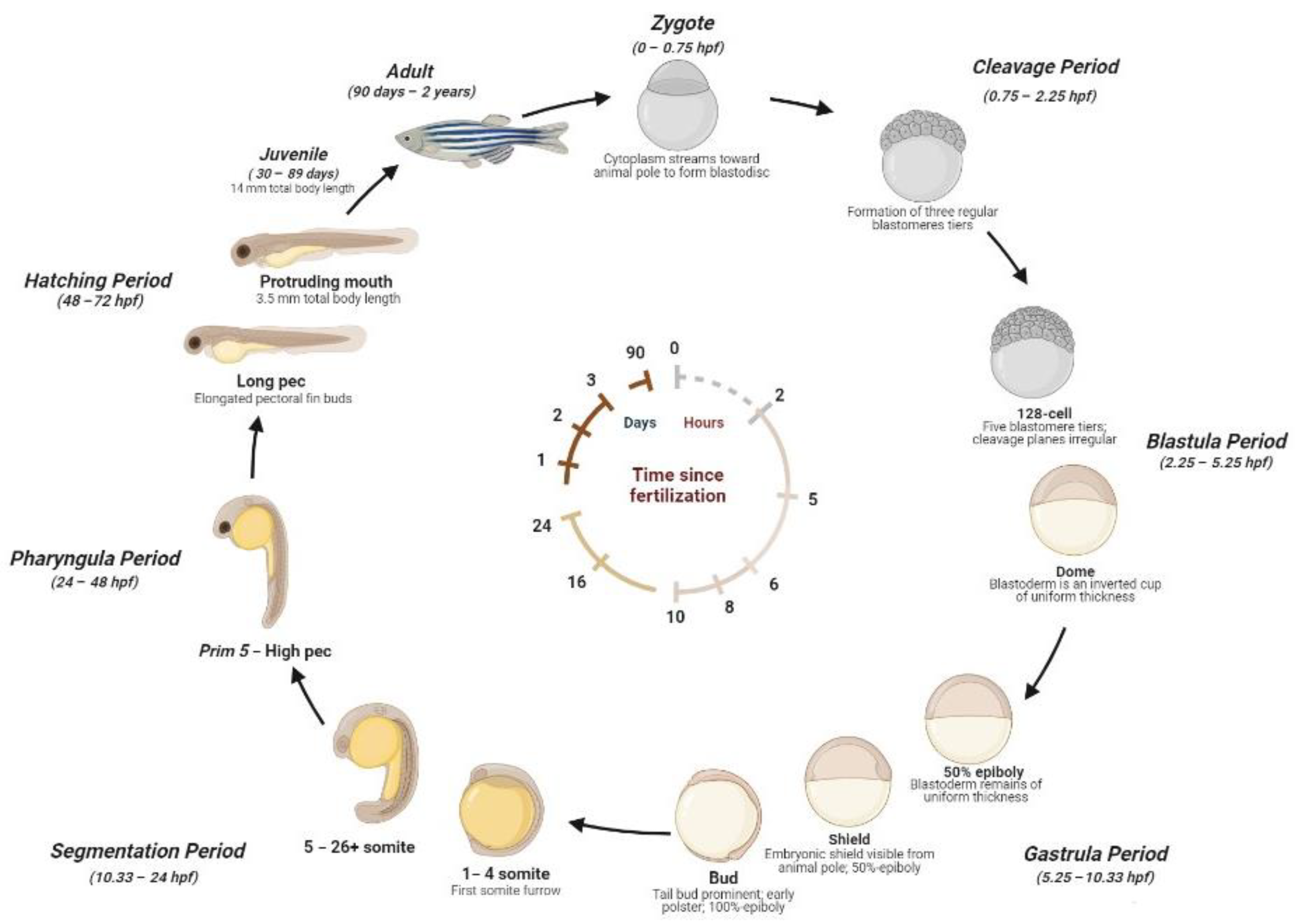
Zebrafish, a popular model organism in developmental biology, offers invaluable insights into the intricate process of axis formation. Among the myriad factors influencing this process, BMP7 stands out as a key player. This protein, part of the Bone Morphogenetic Protein (BMP) family, is essential for establishing the dorsal-ventral (D-V) axis during embryogenesis. Understanding BMP7’s role not only sheds light on zebrafish development but also has broader implications for regenerative medicine and disease research. (zebrafish development, BMP signaling, dorsal-ventral axis)
The Importance of Axis Formation in Zebrafish

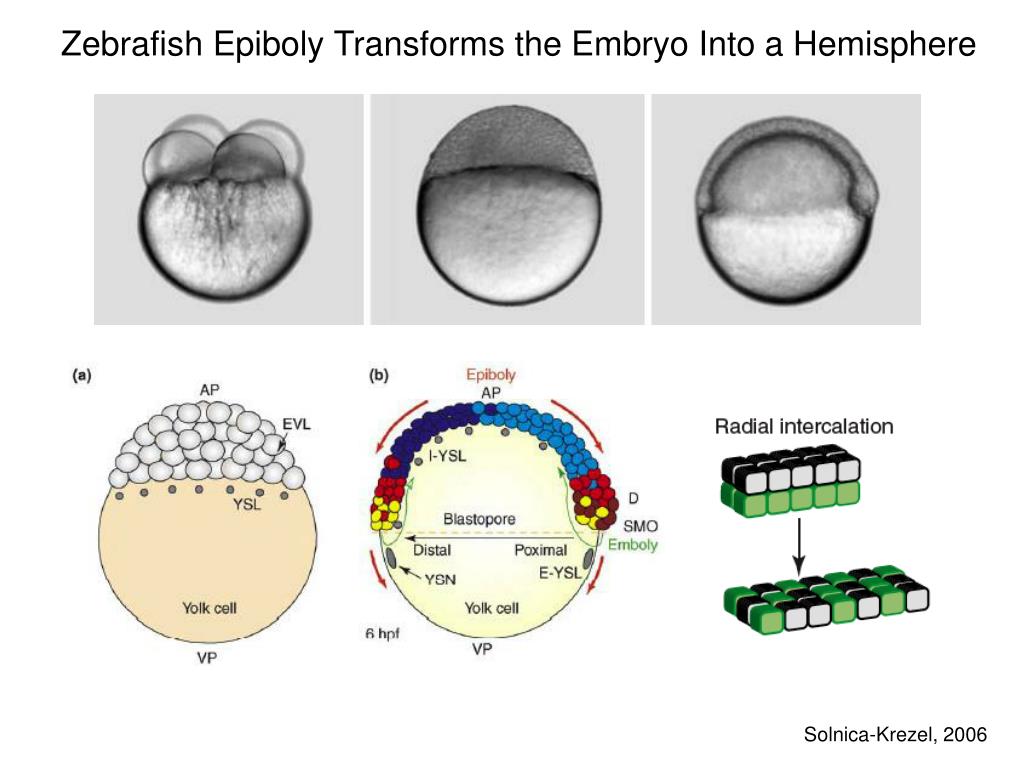
Axis formation is a fundamental step in embryonic development, defining the body plan of an organism. In zebrafish, the D-V axis is established within hours of fertilization, guided by a complex interplay of signaling molecules. BMP7 plays a pivotal role in this process by regulating cell differentiation and tissue patterning. Its precise function ensures that cells develop into the correct structures, laying the foundation for a healthy organism. (embryonic development, tissue patterning, cell differentiation)
BMP7’s Role in Dorsal-Ventral Patterning
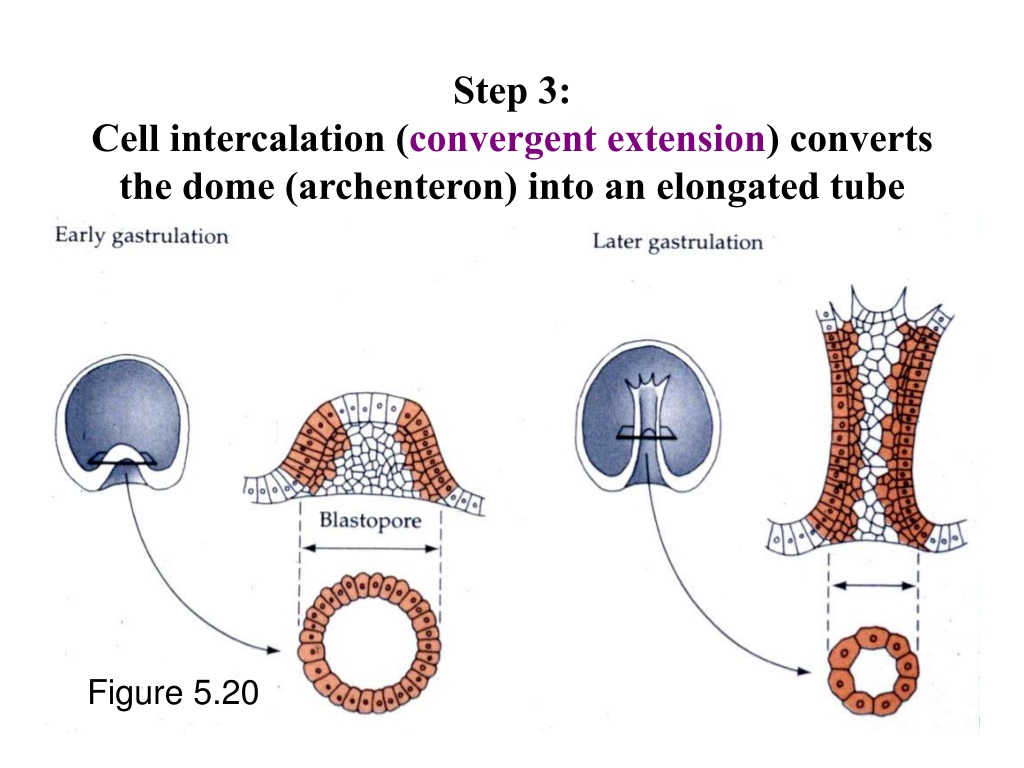
BMP7 acts as a morphogen, creating a gradient of signaling activity that specifies cell fates along the D-V axis. In the ventral region, high BMP7 activity promotes ventral cell identities, while lower levels in the dorsal region allow for dorsal-specific development. This gradient is crucial for the proper formation of organs and tissues. Without BMP7, embryos often exhibit severe patterning defects, highlighting its indispensable role. (morphogen gradient, cell fate specification, patterning defects)
Key Mechanisms of BMP7 Signaling
- Receptor Binding: BMP7 binds to specific receptors on the cell surface, initiating a signaling cascade.
- Smad Activation: This cascade activates Smad proteins, which translocate to the nucleus to regulate gene expression.
- Target Genes: BMP7 signaling upregulates genes involved in ventral development while repressing dorsal-specific genes.
Applications in Research and Medicine
The study of BMP7 in zebrafish has far-reaching implications. Researchers leverage this knowledge to investigate human developmental disorders and spinal cord injuries, where BMP signaling plays a critical role. Additionally, BMP7 is a potential target for therapeutic interventions in regenerative medicine. (regenerative medicine, developmental disorders, therapeutic targets)
💡 Note: Zebrafish models are particularly useful due to their rapid development and transparency, allowing real-time observation of BMP7’s effects.
Checklist for Understanding BMP7’s Role
- Recognize BMP7 as a key morphogen in D-V axis formation.
- Understand its signaling pathway and target genes.
- Appreciate its applications in developmental biology and medicine.
In summary, BMP7 is a critical regulator of zebrafish axis formation, ensuring proper embryonic development through precise signaling gradients. Its role extends beyond basic biology, offering insights into human health and disease. By studying BMP7, researchers unlock new possibilities for therapeutic advancements and a deeper understanding of life’s earliest stages. (BMP7 signaling, embryonic development, therapeutic advancements)
What is BMP7, and why is it important in zebrafish development?
+BMP7 is a protein in the Bone Morphogenetic Protein family that plays a crucial role in establishing the dorsal-ventral axis during zebrafish embryogenesis. It ensures proper cell differentiation and tissue patterning.
How does BMP7 signaling work in zebrafish embryos?
+BMP7 binds to cell surface receptors, activating a signaling cascade that includes Smad proteins. These proteins regulate gene expression, promoting ventral development and repressing dorsal-specific genes.
What are the applications of studying BMP7 in zebrafish?
+Research on BMP7 in zebrafish has applications in understanding developmental disorders, spinal cord injuries, and regenerative medicine, offering potential therapeutic targets.