Biased Signaling Research: UCSF Group Breakthroughs Explained
Recent breakthroughs in biased signaling research by the UCSF group have revolutionized our understanding of cellular communication. By focusing on how cells selectively activate specific pathways, this research opens new avenues for targeted therapies and personalized medicine. This post explores the groundbreaking findings, their implications, and what they mean for the future of medical science,biased signaling research,UCSF breakthroughs,cellular communication.
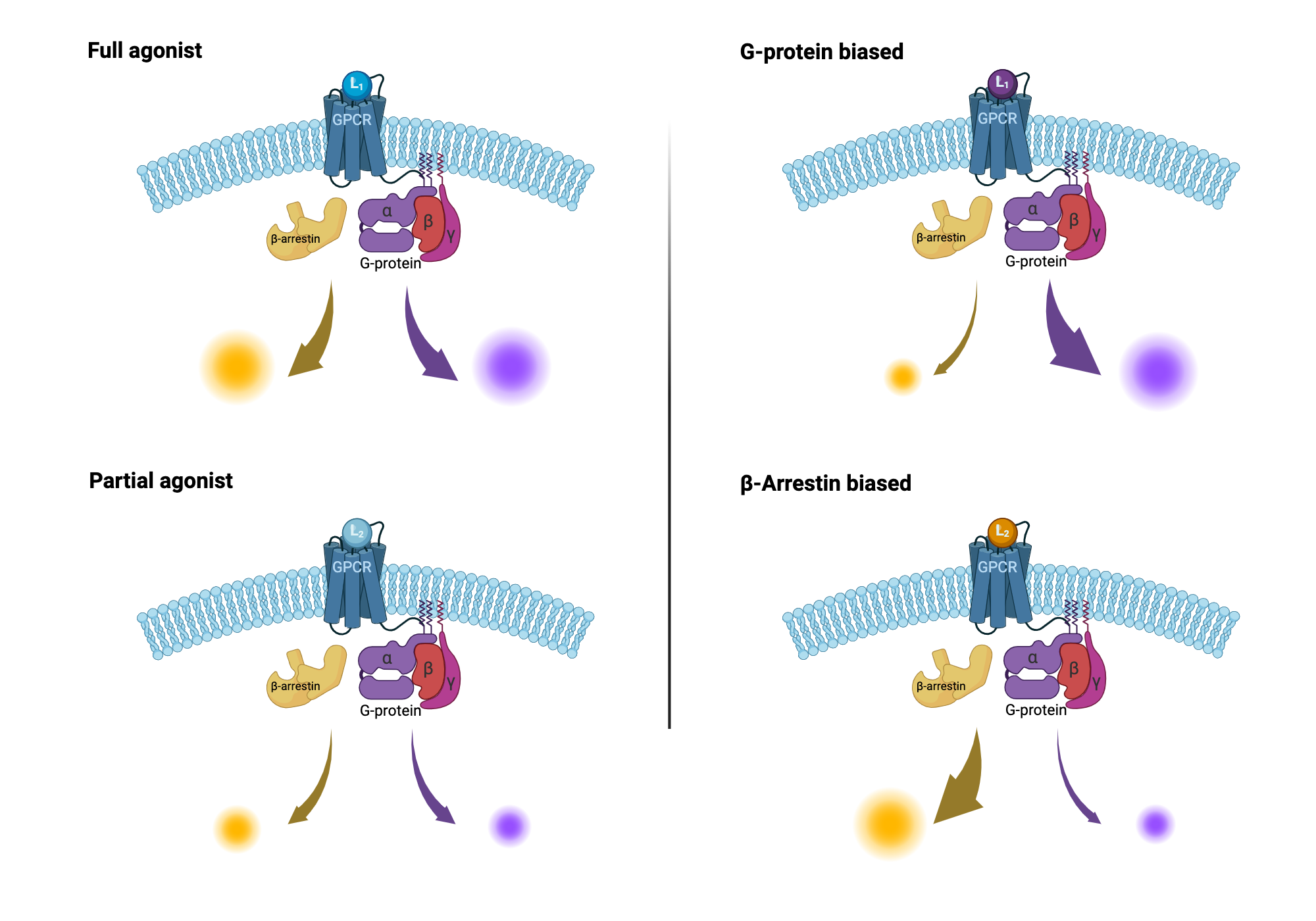
What is Biased Signaling?

Biased signaling refers to the ability of cells to activate specific signaling pathways in response to a ligand, rather than triggering all possible pathways. This mechanism allows for precise control over cellular responses, which is crucial for developing drugs with fewer side effects. The UCSF group’s research has shed light on how this process works at a molecular level,biased signaling mechanisms,molecular biology,drug development.
UCSF Group’s Key Discoveries

The UCSF team has made several pivotal discoveries in biased signaling research:
- Pathway Specificity: Identified how certain ligands preferentially activate specific pathways,biased signaling pathways,ligand interactions.
- Therapeutic Applications: Demonstrated the potential of biased signaling in treating diseases like heart failure and chronic pain,biased signaling therapies,heart failure treatments,chronic pain management.
- Technological Advances: Developed new tools to study biased signaling in real-time,biased signaling tools,real-time cellular analysis.
Implications for Medicine

The UCSF group’s findings have significant implications for the medical field. By understanding biased signaling, researchers can design drugs that target specific pathways, reducing side effects and improving efficacy. This approach is particularly promising for conditions where traditional treatments fall short,biased signaling in medicine,targeted therapies,personalized medicine.
Potential Applications
| Disease | Potential Therapy |
|---|---|
| Heart Failure | Biased agonists to protect cardiac tissue |
| Chronic Pain | Selective opioid receptor activation |
| Cancer | Targeted pathway inhibition |

📌 Note: While biased signaling shows promise, further clinical trials are needed to validate its safety and efficacy,clinical trials,safety and efficacy.
Key Takeaways Checklist

- Biased signaling allows cells to activate specific pathways selectively.
- UCSF research highlights pathway specificity and therapeutic potential.
- New tools enable real-time study of biased signaling.
- Applications include heart failure, chronic pain, and cancer treatments.
The UCSF group’s breakthroughs in biased signaling research mark a significant leap forward in understanding cellular communication. With potential applications in targeted therapies and personalized medicine, this research paves the way for more effective and safer treatments. As studies continue, we can expect even more transformative discoveries in this field,biased signaling research,UCSF breakthroughs,cellular communication,targeted therapies,personalized medicine.
What is biased signaling?
+
Biased signaling is a process where cells selectively activate specific pathways in response to a ligand, allowing for precise control over cellular responses,biased signaling definition,cellular pathways.
How does biased signaling benefit drug development?
+
By targeting specific pathways, biased signaling enables the development of drugs with fewer side effects and improved efficacy,biased signaling in drug development,drug efficacy,side effect reduction.
What are the key discoveries of the UCSF group?
+
The UCSF group identified pathway specificity, demonstrated therapeutic applications, and developed tools for real-time analysis of biased signaling,UCSF discoveries,pathway specificity,therapeutic applications.


