Redwoods and Their Homologous Organisms Explained

Redwoods, the towering giants of the forest, have captivated nature enthusiasts and scientists alike for centuries. Known for their immense height and longevity, these trees are not just marvels of nature but also share fascinating similarities with other organisms through homologous structures. Understanding these connections sheds light on the evolutionary journey of plants and animals. In this post, we’ll explore the world of redwoods and their homologous organisms, uncovering the secrets behind their shared traits and significance in the natural world, redwood trees, homologous structures, evolutionary biology.
What Are Redwoods and Why Are They Unique?
Redwoods, scientifically known as Sequoia sempervirens, are among the tallest and oldest trees on Earth. Found primarily in the coastal regions of California and Oregon, these trees can reach heights of over 350 feet and live for thousands of years. Their thick, fire-resistant bark and ability to thrive in foggy climates make them uniquely adapted to their environment, redwood forest, coastal ecosystems.
Homologous Structures: A Key to Understanding Evolution
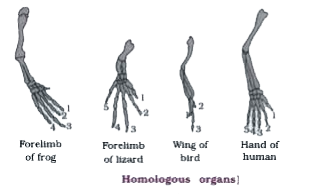
Homologous structures are body parts in different organisms that share a common ancestor but may serve different functions. For instance, the forelimbs of humans, birds, and bats are homologous, as they all evolved from a shared ancestral structure. In plants, homologous structures can be seen in the leaves, stems, and roots of different species, plant evolution, comparative anatomy.
Redwoods and Their Homologous Organisms
Redwoods share homologous traits with other coniferous trees, such as pines and spruces. These include needle-like leaves, cone-bearing reproductive structures, and woody trunks. These features evolved from a common ancestor, highlighting the interconnectedness of plant species, coniferous trees, evolutionary adaptations.
| Organism | Homologous Structure | Function |
|---|---|---|
| Redwoods | Needle-like leaves | Photosynthesis and water conservation |
| Pines | Needle-like leaves | Photosynthesis and water conservation |
| Spruces | Needle-like leaves | Photosynthesis and water conservation |

The Significance of Homologous Structures in Redwoods
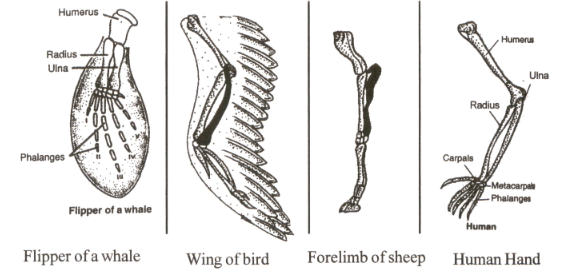
Studying homologous structures in redwoods provides insights into their evolutionary history and survival strategies. For example, their needle-like leaves are adapted to minimize water loss, a trait shared with other conifers in arid environments. This highlights how evolution shapes organisms to thrive in specific habitats, evolutionary adaptations, plant survival strategies.
📌 Note: Homologous structures are distinct from analogous structures, which have similar functions but different evolutionary origins.
How to Experience Redwoods and Their Homologous Organisms
For those eager to witness these majestic trees and their homologous counterparts, visiting redwood forests or botanical gardens is a must. Guided tours and educational programs offer a deeper understanding of their ecological importance. Additionally, consider planting coniferous trees in your garden to observe homologous traits firsthand, eco-tourism, botanical gardens.
Checklist for Exploring Redwoods and Homologous Organisms
- Visit a redwood forest or national park.
- Identify homologous structures in different coniferous trees.
- Participate in guided tours or workshops on plant evolution.
- Plant coniferous trees in your garden for hands-on observation.
Redwoods and their homologous organisms offer a window into the intricate world of evolutionary biology. By understanding their shared traits, we gain a deeper appreciation for the natural world and the processes that shape life on Earth. Whether you’re a nature enthusiast or a curious learner, exploring these connections is both enlightening and inspiring, evolutionary biology, nature exploration.
What are redwoods?
+
Redwoods (Sequoia sempervirens) are among the tallest and oldest trees on Earth, primarily found in California and Oregon.
What are homologous structures?
+
Homologous structures are body parts in different organisms that share a common ancestor but may serve different functions.
Why are redwoods important?
+
Redwoods are crucial for their ecological role, carbon sequestration, and insights into plant evolution.