Degradation Models in Digital Twin Technology: Real-World Examples
In the rapidly evolving world of Digital Twin Technology, degradation models play a pivotal role in predicting and managing the lifecycle of physical assets. By simulating wear and tear, these models enable industries to optimize maintenance, reduce downtime, and enhance efficiency. This blog explores real-world examples of degradation models in digital twins, shedding light on their applications and benefits. Whether you're an industry professional or a tech enthusiast, understanding these models can unlock new possibilities for asset management and innovation.
Understanding Degradation Models in Digital Twins
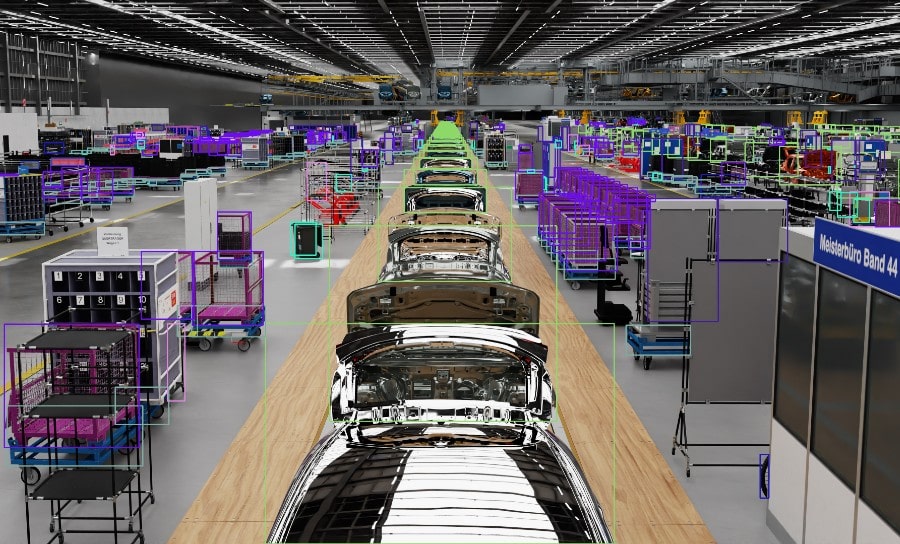

Degradation models are algorithms that simulate how physical assets deteriorate over time due to factors like usage, environmental conditions, and material fatigue. In Digital Twin Technology, these models create virtual replicas of assets, allowing for real-time monitoring and predictive analysis. By integrating data from sensors and historical records, degradation models provide actionable insights into asset health and performance.
📌 Note: Degradation models are essential for industries like manufacturing, energy, and transportation, where asset longevity directly impacts operational efficiency.
Real-World Applications of Degradation Models

1. Predictive Maintenance in Manufacturing
In manufacturing, degradation models help predict machinery failures before they occur. For instance, a digital twin of a CNC machine can simulate wear on its cutting tools, enabling scheduled maintenance and minimizing production halts. Companies like Siemens use this approach to reduce unplanned downtime by up to 50%.
2. Infrastructure Monitoring in Construction
Digital twins of bridges and buildings incorporate degradation models to assess structural integrity over time. By analyzing factors like corrosion and material fatigue, engineers can prioritize repairs and ensure safety. The Golden Gate Bridge in San Francisco utilizes such models for long-term maintenance planning.
3. Energy Sector Optimization
In the energy sector, degradation models are applied to wind turbines and solar panels to predict performance decline. For example, Vestas uses digital twins to optimize turbine maintenance schedules, increasing energy output and extending asset lifespan.
| Industry | Application | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing | Predictive Maintenance | Reduced Downtime |
| Construction | Infrastructure Monitoring | Enhanced Safety |
| Energy | Asset Performance Optimization | Increased Efficiency |

Implementing Degradation Models in Your Business

Adopting degradation models in digital twins requires a strategic approach. Here’s a checklist to guide your implementation:
- Assess Asset Criticality: Identify which assets would benefit most from degradation modeling.
- Invest in IoT Sensors: Ensure real-time data collection for accurate simulations.
- Choose the Right Software: Select digital twin platforms with robust degradation modeling capabilities.
- Train Your Team: Equip employees with the skills to interpret and act on model insights.
Degradation models in Digital Twin Technology are transforming how industries manage and maintain their assets. From manufacturing to energy, these models offer unparalleled insights into asset health, enabling proactive decision-making and cost savings. By understanding and implementing these models, businesses can stay ahead in an increasingly competitive landscape. (Digital Twin Technology, Degradation Models, Predictive Maintenance)
What are degradation models in digital twins?
+
Degradation models are algorithms that simulate asset wear and tear over time, enabling predictive maintenance and lifecycle management in digital twins.
Which industries benefit most from degradation models?
+
Industries like manufacturing, construction, and energy benefit significantly due to their reliance on heavy machinery and infrastructure.
How do I start implementing degradation models?
+
Begin by assessing asset criticality, investing in IoT sensors, choosing the right software, and training your team for effective implementation.